Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR Spectroscopy is not limited to the study of protons. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy.
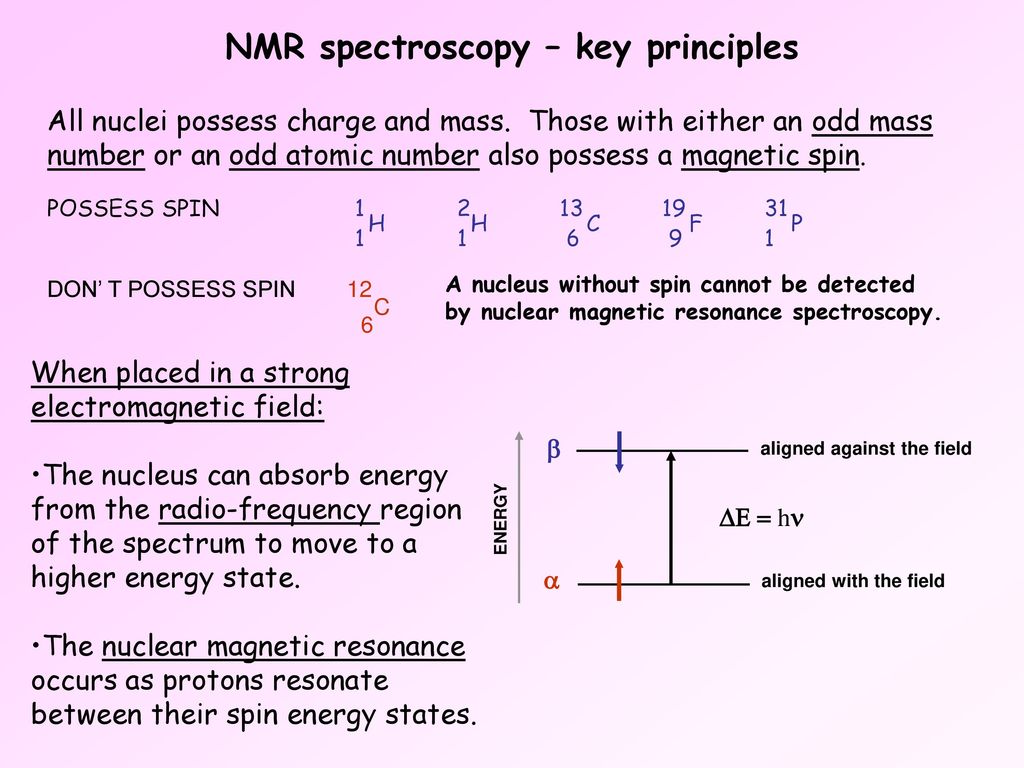
Nmr Spectroscopy Key Principles Ppt Download
This review aims at presenting in an accessible manner the requirements and limitations of this technique.
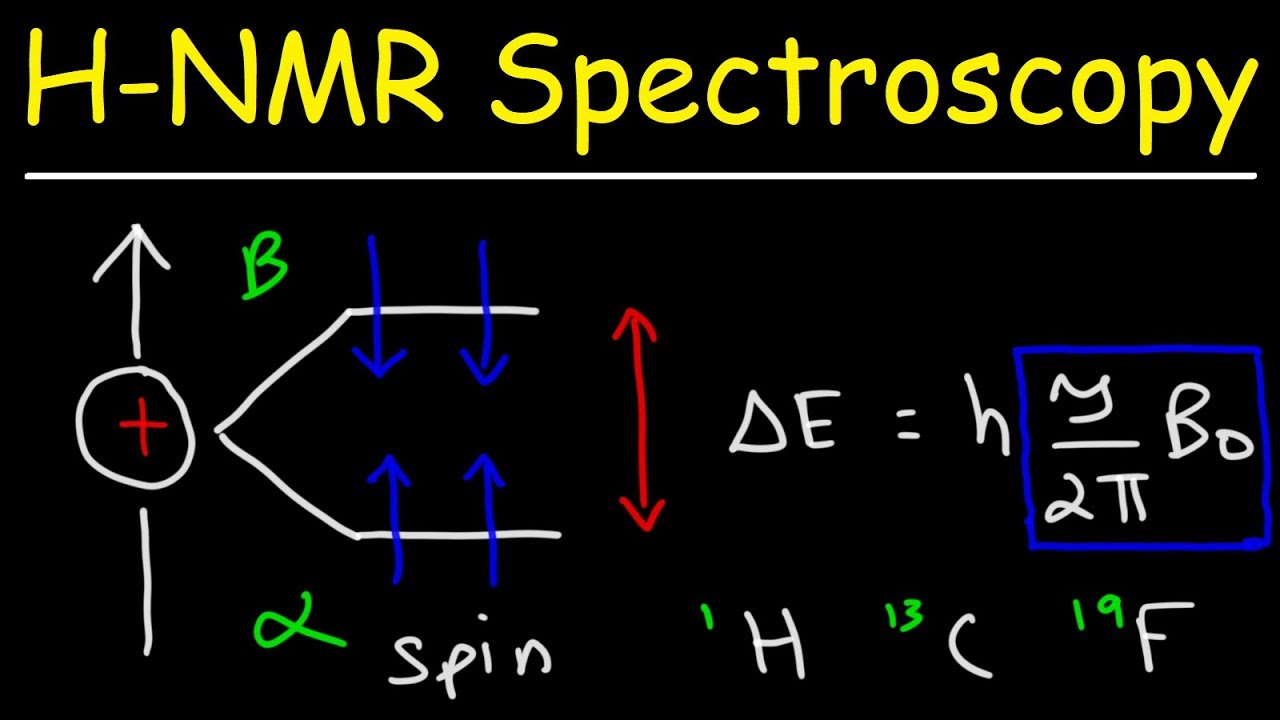
. Basic Principle of NMR In order to generate an NMR spectrum the nucleus must contain a net spin. The application of NMR spectroscopy to the study of proteins and nucleic acids has provided unique in- formation on the dynamics and chemical kinetics of these systems. The nuclei of many elements such as 13 C spin generating a magnetic field.
It is used to determine the molecular structure at the atomic level of a sample. NMR spectroscopy is a powerful tool for biologists interested in the structure dynamics and interactions of biological macromolecules. PowersProgress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 100 2017 116.
The applications of MRS as a research tool are extremely diverse encompassing studies on isolated cells body fluids and perfused organs at high magnetic field strengths in an experimental. Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy is a versatile tool that provides information on structures and dynamics of various biological and synthetic molecules at an atomic level. There are two major relaxation processes.
13 C Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Tutorial Key Concepts Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy or NMR Spectroscopy can be used to identify any isotope unless the isotope has both an even number of protons and an even number of neutrons. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 79 2014 1447 23. For the four common nuclei noted above the magnetic moments are.
Apart from the molecular structure NMR spectroscopy can determine phase changes conformational and configurational alterations solubility and diffusion potential Krishnan 2019. 12 based on residual quadrupolar coupling of the form of Eq. As an introduction the history of NMR will highlight how the method evolved from physics to chemistry and finally to biology over.
1 H μ 27927 19 F μ 26273 31 P μ 11305 13 C μ 07022. Lipidomics is the -omics science that pursues the comprehensive characterization of lipids present in a biological sample. On this page we will cover the basic theory behind the technique.
Welcome to the WSU Center for NMR Spectroscopy To combat the spread of COVID-19 effective September 8 2021 there is a more stringent procedure for using the NMR lab. One is 12 which is anti-parallel to the magnetic field and the other is 12 which is parallel to the magnetic field. Carbon Nuclear Magnetic Resonance 13C-NMR Spectroscopy.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance NMR Spectroscopy is a technique used for determining the structure of organic compounds. The following diagram gives the approximate frequencies that correspond to the spin state energy separations for each of these nuclei in an external magnetic field of 235 T. The height of each step is proportional to the area under the resonance.
Theory Some nuclei possess a magnetic moment - such as a hydrogen nucleus 1H or a carbon nucleus 13C. Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy tutorial all along with the key concepts of Basic Principle of NMR The Source of NMR Spectra NMR spectrum Pattern of the Spectrum The. E2 12 γh 2Π H0.
He is also Director of the Magnetic Resonance Laboratory a research and. Carbon-13 has a nuclear spin I ½ and makes up 11 of all naturally occurring carbon a high enough abundance along with. The chemical environment of specific nuclei is deduced from information obtained.
A powerful technique useful for identifying the small to the very large When some atoms are placed in a strong magnetic field their nuclei behave like tiny bar magnets aligning themselves with the field. These moments are in nuclear magnetons which are 50507810-27 JT-1. The area under an NMR resonance is proportional to the number of nuclei that give rise to that resonance.
Metabolomics data and has contributed to the observed increase in NMR-based metabolomics studies. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy tutorial. It is important to remember that with NMR we are performing experiments on the nuclei of atoms not the electrons.
Copyright 1997-2019 JP. 1H NMR is used to determine the type and number of H atoms. Introduction Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy explores the electronic environment of atoms.
Nuclear Magnetic Resonance spectroscopy is a powerful and theoretically complex analytical tool. For scientists to be able to measure the exact structure of compounds to understand their properties is key. Any element with a nuclear spin 13 C 17 O 19 F 31 P and many others will give rise to an NMR signal.
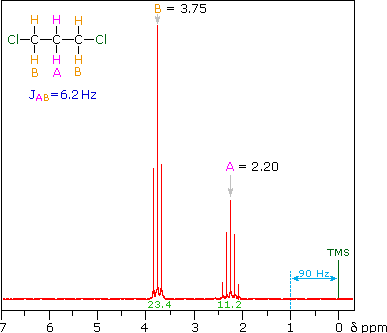
Despite these advancements one-dimensional 1D 1H NMR spectra are still hindered by a sig-. Mass spectrometry MS is an analytical technique that is used to measure the mass-to-charge ratio of ionsThe results are presented as a mass spectrum a plot of intensity as a function of the mass-to-charge ratioMass spectrometry is used in many different fields and is applied to pure samples as well as complex mixtures. 2 6 integral d 36 d 12 The relative area under the resonances at d 36 and 12 is 13 The integral is superimposed over the spectrum as a stair-step line.
Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy is a technique that is depends on quantization of the spin angular momentum of the nucleus. Two common types of NMR spectroscopy are used to characterize organic structure. For a nucleus to have spin it must contain an odd mass number.
Different analytical strategies such as nuclear magnetic resonance or mass spectrometry with or without previous chromatographic separation are currently used to analyze the lipid composition of a sample. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI and magnetic resonance spectroscopy MRS. The SCSB NMR Laboratory is located in its own two-story building NMR Dockside Building on the UTMB campus at GalvestonCurrently the following three high-field NMR spectrometers are.
Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR spectroscopy is an advanced characterization technique. Hornak is Professor of Chemistry and Imaging Science at the Rochester Institute of Technology where he teaches courses in magnetic resonance imaging nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy analytical chemistry and physical chemistry. Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy is a powerful analytical technique used to characterize organic molecules by identifying carbon-hydrogen frameworks within molecules.
Nuclear magnetic resonance NMR is a spec- troscopic technique that detects the energy ab- sorbed by changes in the nuclear spin state. Full solution of the evolution equations In this section we provide the complete solution of the evolu- tion equation Eq. The biomedical applications of nuclear magnetic resonance NMR are twofold.
11 and a fluctuating quadrupolar interaction of the. H0 is magnetic field which separates the energy into two.

Analytical Chemistry A Guide To Proton Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Nmr Compound Interest
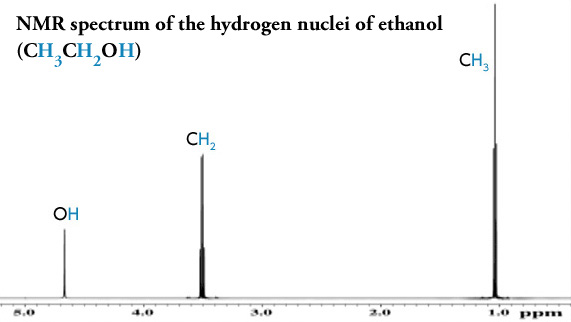
Nmr Basic Knowledge Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer Nmr Products Jeol

Nmr Spectroscopy In Easy Way Part 1 Youtube
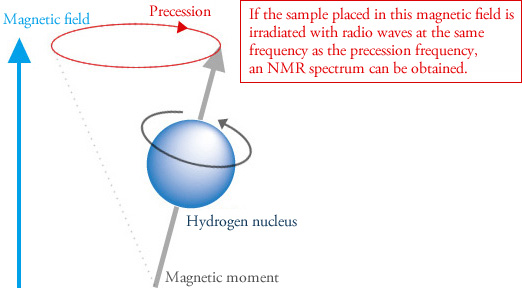
Nmr Basic Knowledge Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectrometer Nmr Products Jeol


0 comments
Post a Comment